In general a 2k-p design is a frac12p fraction of a 2k design using 2k-p runs. Choose Home Insert Standard Design to add a standard design folio to the current project.

5 4 7 1 Full Factorial Example
For 2kdesigns the use of the ANOVA is confusing and makes little sense.

. Click Design Type in the folios navigation panel and then select Two Level Factorial in the input panel. This design is called a 25 1 fractional factorial design. Fractional Factorial Designs Example 2 Filtration rate experiment.
The Advantages and Challenges of Using Factorial Designs. Traditional research methods generally study the effect of one variable at a time because it is statistically easier to manipulate. For example runs 2 and 4 represent factor A at the high level.
Note that the row headings are not included in the Input Range. A design with p such generators is a 1l pl p fraction of the full factorial design. Misuse of the ANOVA for 2k.
A factorial design is often used by scientists wishing to understand the effect of two or more independent variables upon a single dependent variable. Neffect24 divided by df1 and turned into an F-ratio. Now choose the 2k Factorial Design option and fill in the dialog box that appears as shown in Figure 1.
As an example of a factorial design involving two factors an engineer is designing a battery for use in a device that will be subjected to some extreme variations in tempera- ture. A factorial experiment is carried out in the pilot plant to study the factors thought to influence the filtration rate of this product. A 2 2 factorial design has four conditions a 3 2 factorial design has six conditions a 4 5 factorial design would have 20 conditions and so on.
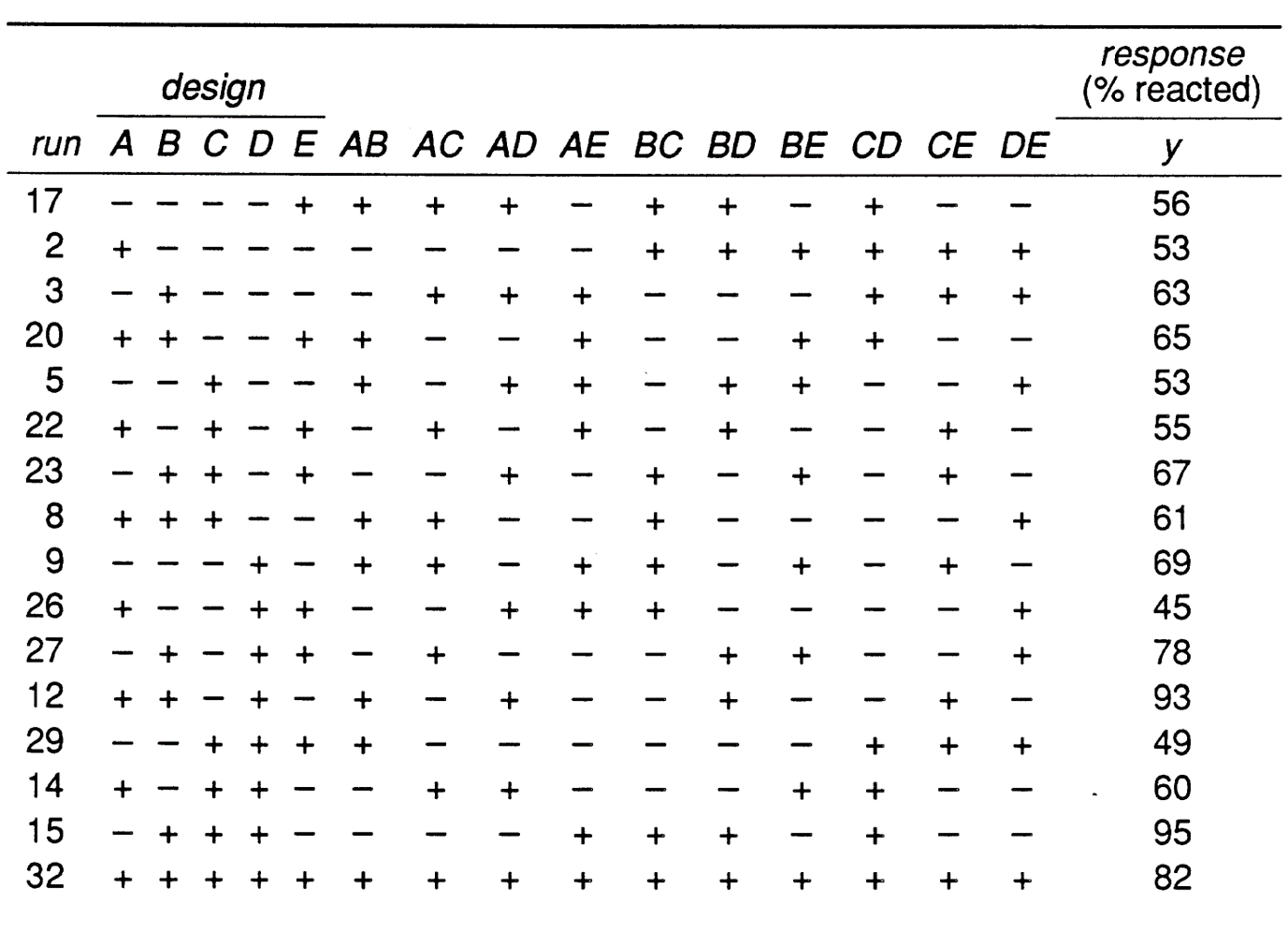
The average response from these runs can be contrasted with those from runs 1. Only 14 were run. Recall that there are four factors in the experimentA B C and D each of 2 levels.
Rather than the 32 runs that would be required for the full 2 5 factorial experiment this experiment requires only eight runs. Partitioned into individual SS for effects each equal to. In this type of design one independent variable has two levels and the other independent variable has three levels.
4 FACTORIAL DESIGNS 41 Two Factor Factorial Designs A two-factor factorial design is an experimental design in which data is collected for all possible combinations of the levels of the two factors of interest. A full factorial for the five factors A B C D E would have needed 25 32 runs. This design is called a 2 1 fractional factorial design.
Full factorial is 2k Fractional Factorial is 2kp Degree of fraction is 2p 25-5 Half-Fraction 2k Factorials This is one half the usual number of runs Similar to blocking procedure Choose a generator which divides efiects into two Based on pluses and minuses of one factor Deflning Relation. For example a 2 5 2 design is 14 of a two level five factor factorial design. Figure 1 2k Factorial Design dialog box.
A 23 factorial design is a type of experimental design that allows researchers to understand the effects of two independent variables on a single dependent variable. 2 4 full factorial design consists of all the 16 level combinations of the four factors. So for example a 43 factorial design would involve two independent variables with four levels for one IV and three levels for the other IV.
If equal sample sizes are taken for each of the possible factor combinations then the design is a balanced two-factor factorial design. Figure 2 2k Factorial Design data analysis tool. Rename the response by clicking Response 1 in the navigation panel and entering Thickness in the input panel.
Also notice that each number in the notation represents one factor one independent variable. One of the big advantages of factorial designs is that they allow researchers to look for interactions between independent variables. This design is called a quarter fraction of the full 25 or a 25-2 design a two to the five minus two design.
A 12 fraction can be generated from any interaction but using the highest-order interaction is the. Suppose the available resource is enough for conducting 8 runs. Upon pressing the OK button the output in Figure 2 is displayed.
We need to choose half. Suppose there are 5 factors of interest A B C D and E and there are only enough resources for 16 experimental runs. Thus we want to run a 12 fraction of a 25 design.
3-2 The points for the factorial designs are labeled in a standard order starting with all low levels and ending with all high levels. For example suppose a botanist wants to understand the effects of sunlight low vs. However in many cases two factors may be interdependent and.

2 K Factorial Design Tool Real Statistics Using Excel
Two Level Factorial Experiments Reliawiki

Full Factorial Design For 2 Factors And 2 Levels A Design Matrix Download Scientific Diagram
Suppose The Experiment Was Ran With A Single Chegg Com

R How To Simulate An Unreplicated Factorial Design Cross Validated
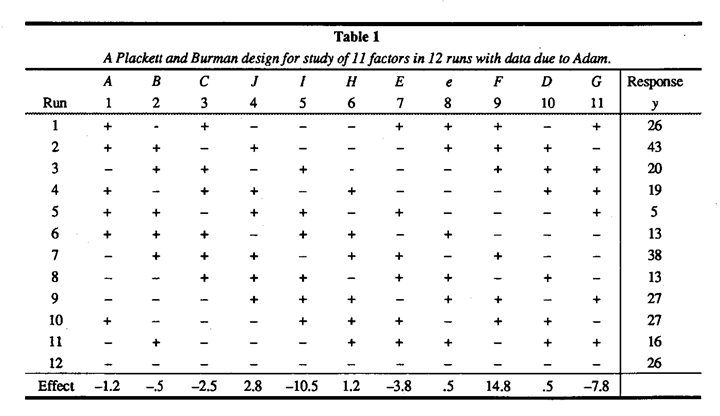
What Can You Find Out From 12 Experimental Runs By George Box And Soren Bisgaard
0 comments
Post a Comment